Parallel imaging is an image reconstruction technique where the k-space data are purposefully undersampled, causing aliasing artifacts, which can be resolved using the spatial information from the receiver coil array. Parallel imaging is often used to accelerate image acquisition or provide high-resolution images without increasing scan time.. Parallel imaging is a widely used technique where the known placement and sensitivities of receiver coils are used to assist spatial localization of the MR signal. Having this additional information about the coils allows reduction in number of phase-encoding steps during image acquisition. This, in turn, potentially results in a several-fold reduction in imaging time.
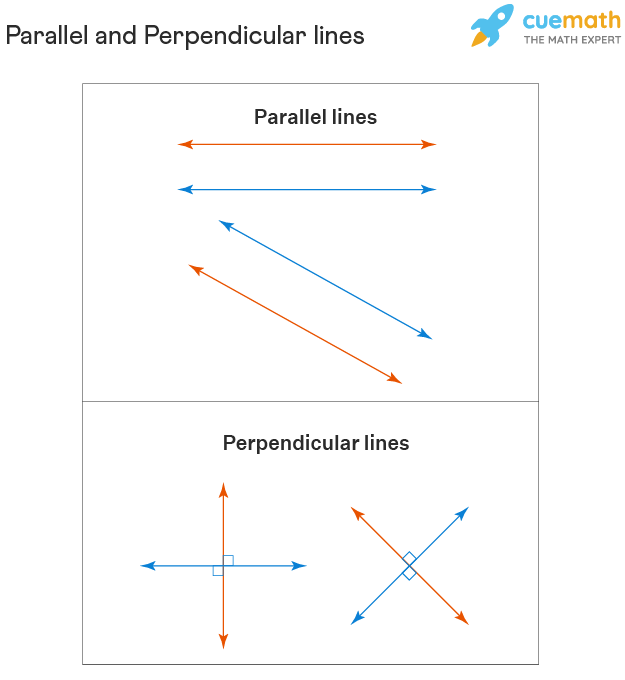
Definition Of Perpendicular Lines
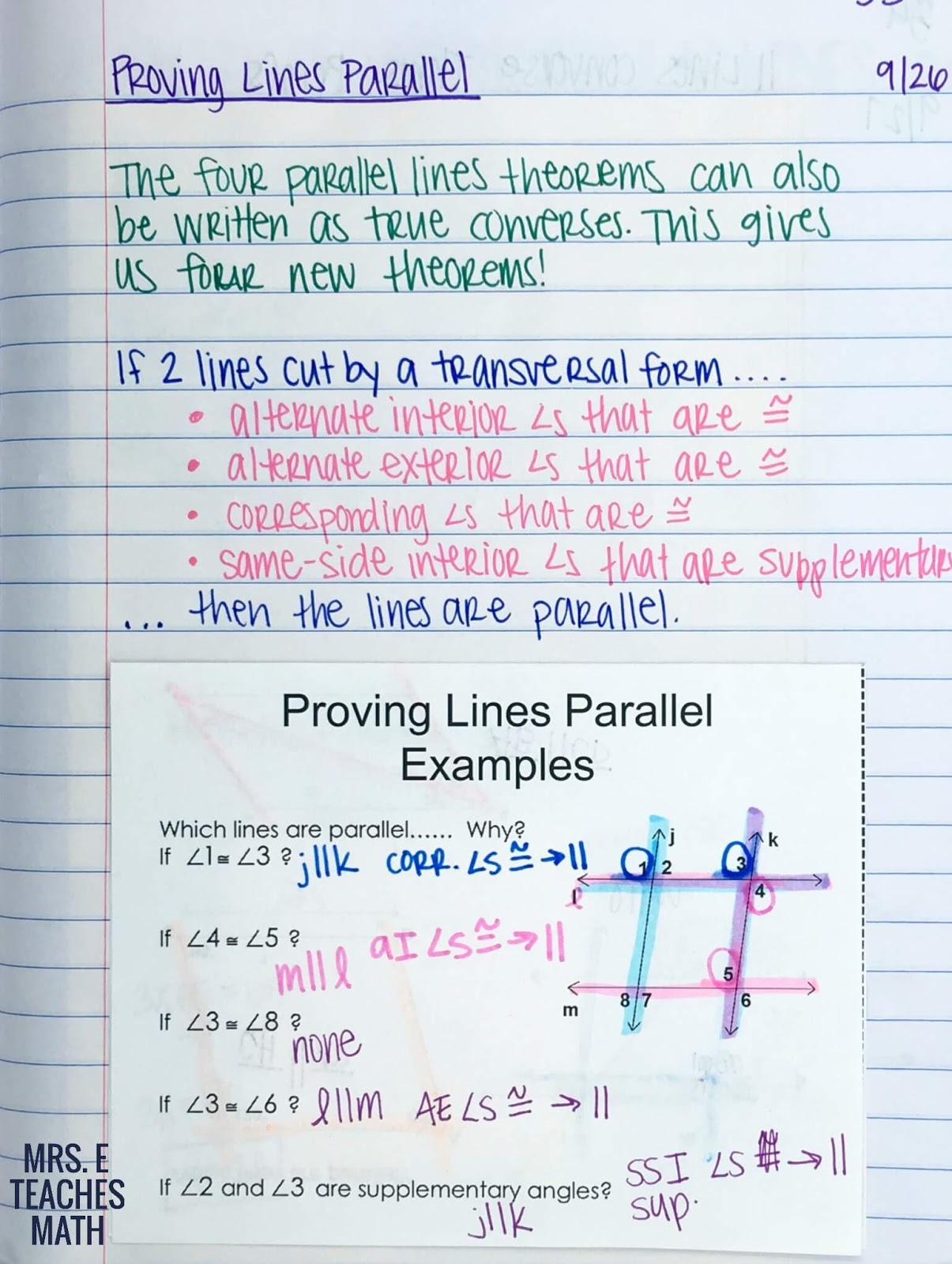
Prove Lines Are Parallel Worksheet
Define Parallel Lines

Geometry Proofs with Parallel Lines Do we have Parallel Lines? YouTube

Parallel Definition Math at Robert Brady blog
Grade 4 Angles Jeopardy Template

Parallel Vs Perpendicular Lines Activity

Parallel, Perpendicular and Intersecting Lines Worksheets

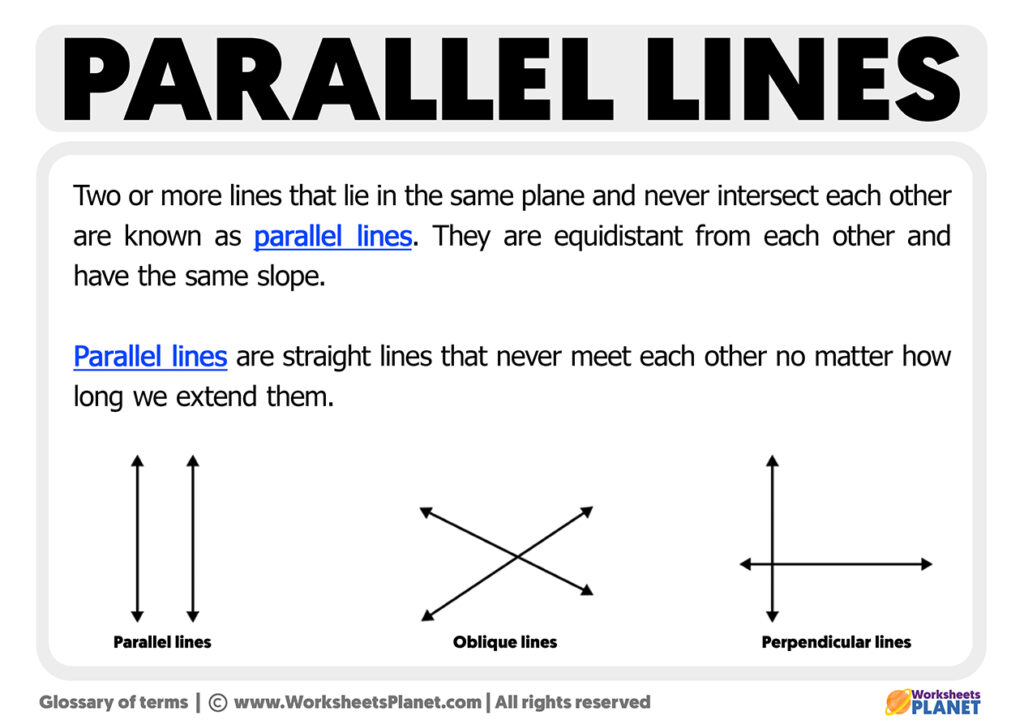
Parallel lines Definition, Properties What are Parallel Lines?

Definition Of Parallel Circuit In Physics Wiring Draw And Schematic
parallelogram a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides

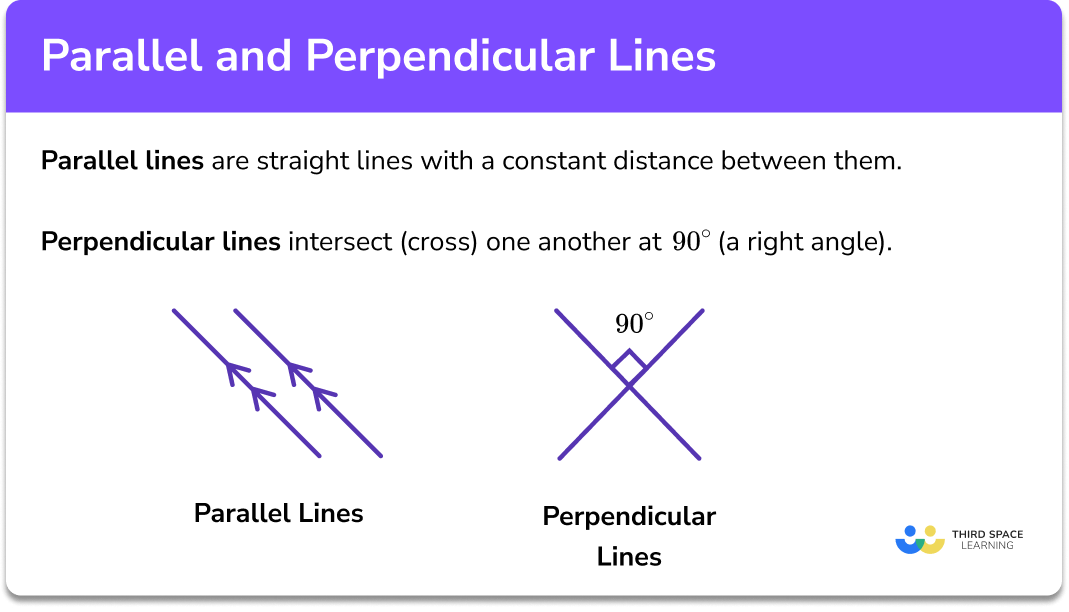
Perpendicular and Parallel
Twality Math Vocab Jeopardy Template

Lessons Passy’s World of Mathematics Mathematics Help Online Page 14

Parallelism Examples

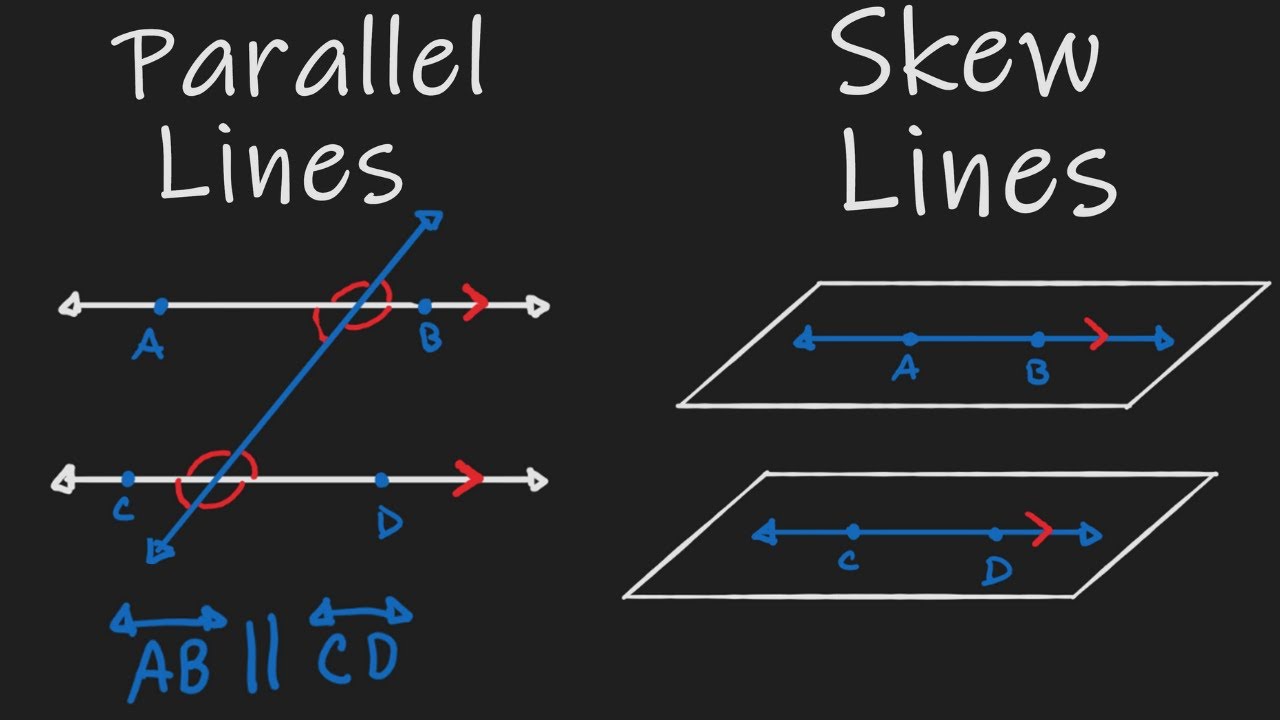
Lines and Types in Mathematics
Parallel Lines Examples In Home at Spencer Weedon blog

Math Worksheets Parallel, Perpendicular, Intersecting Geometry
39 Facts About Parallel

Circuit Diagram Parallel Parallel Lighting Circuit Diagram
1. Introduction Parallel imaging exploits the difference in sensitivities between individual coil elements in a receive array to reduce the number of gradient encoding steps required for imaging. Parallel imaging was originally conceived [1-3] as a means of ultrafast imaging using a single echo readout, replacing gradient phase encoding entirely with spatial encoding using the coil.. Parallel imaging techniques in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offer faster scans by collecting data from multiple receiver coils simultaneously. However, they come with drawbacks. One significant disadvantage is the emergence of parallel imaging artifacts, compromising image quality. Noise amplification artifact arises from the reconstruction of high-frequency information from aliased.